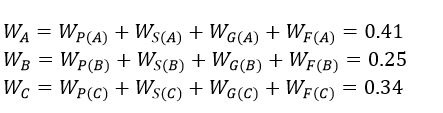Solving an Example Using the OPA
Here, we are going to solve the first example from Ordinal Priority Approach (OPA) in Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis for the scholars who want to employ the OPA in their papers. This example is related to purchasing a car by considering the following attributes:
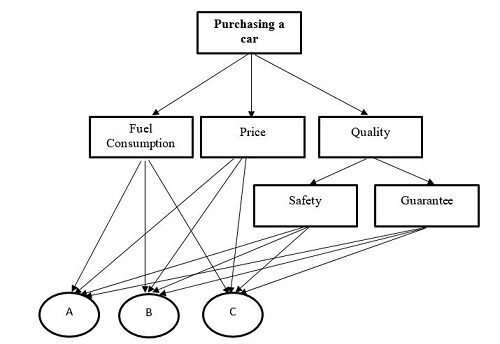
It should be noted that there are three alternatives entitled A, B, and C. After identifying the attributes and alternatives, we should collect the data from the expert. The input data for this example are as follows:
The rank of alternatives:
As can be seen from the above table, the expert declared that the order of the attributes is P=1, S =2, G =3, F=4. Moreover, the order of the alternatives in each attribute was provided. For example, in attribute P, we have A=1, C=2, B=3. After collecting data, the OPA model should be constructed as follows:
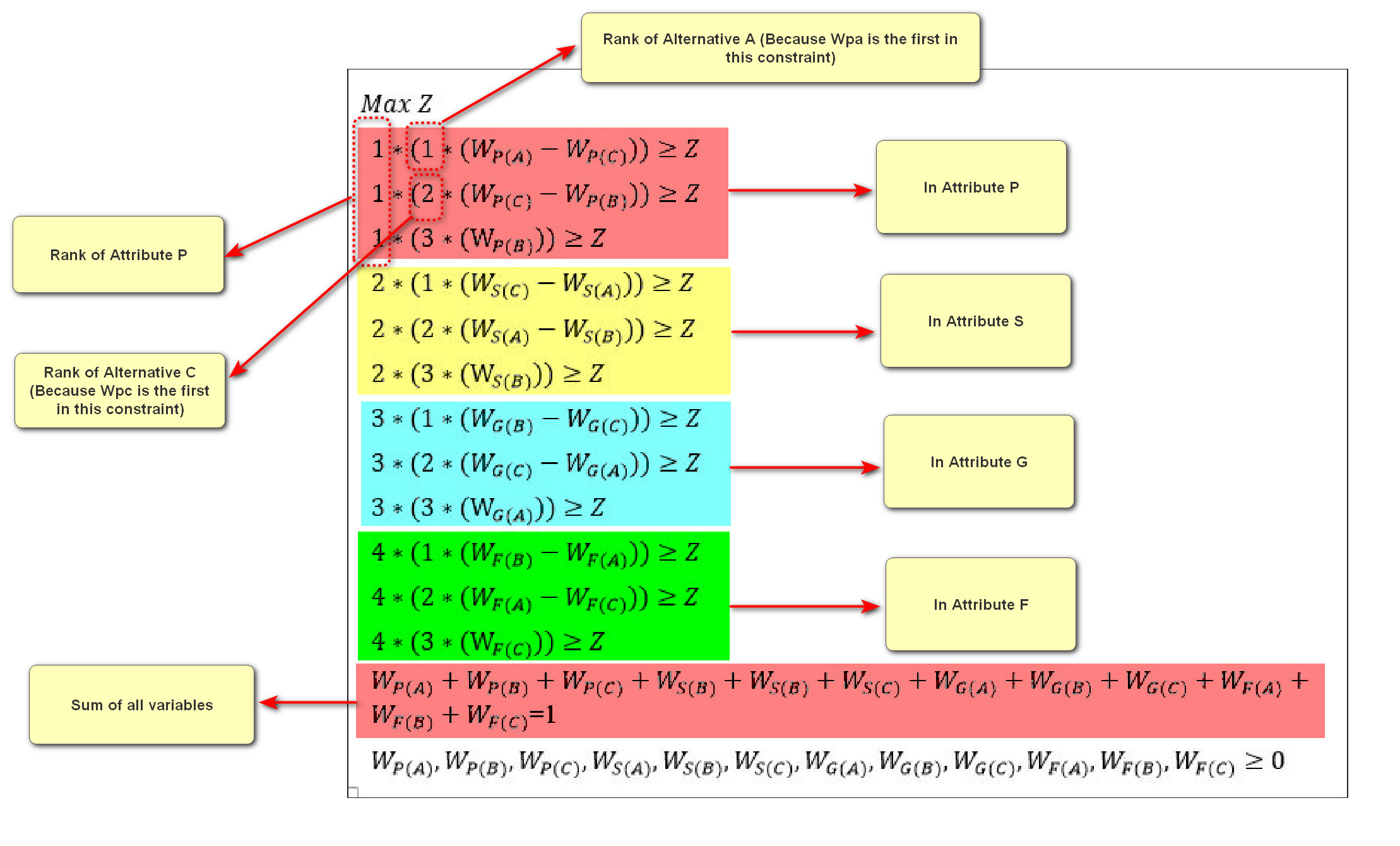
This is a linear model which can be solved using various software such as GAMS, LINGO, Excel, etc. Here, we used LINGO software:
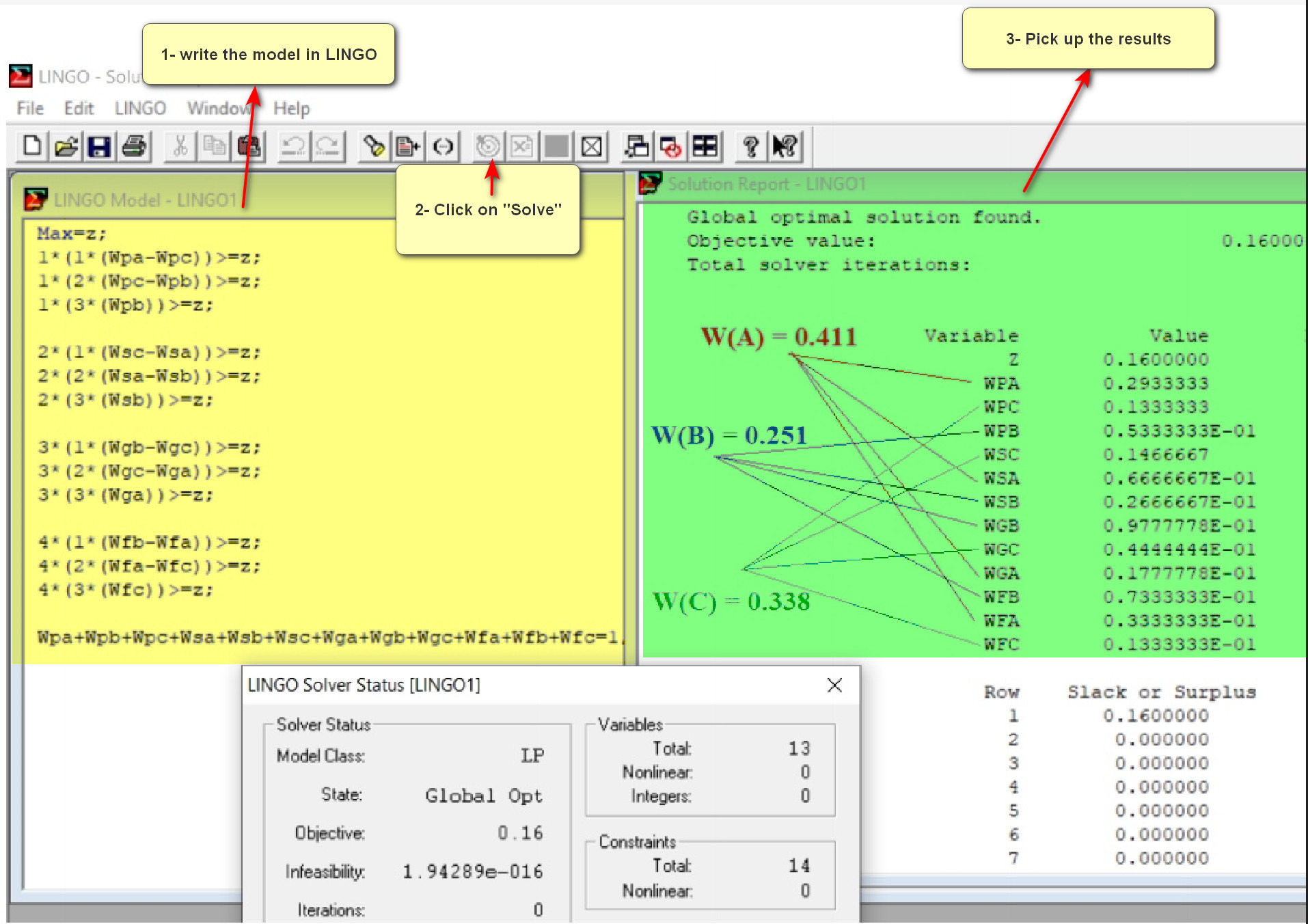
Then, the weight of the attributes can be calculated as follows:
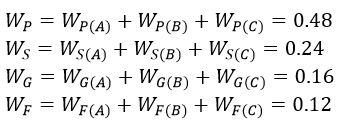
Likewise, the weight of the alternatives can be calculated as follows: